

Holistic Medicine Series Handout #5 - Holistic THYROID Health & Support
Holistic Medicine Series HANDOUT Thursday - April 16, 2009
*** Session #5 ***
Holistic Thyroid Health & Support (these are my more detailed notes)
Aumdoc (Richard J. Clofine, D.O.) 770-633-4257
aumdoc@aumdoc.com WWW.AUMDOC.COM
(Opening Intention)
Thyroid Gland
Physical Anatomy
Energy Anatomy
Physiologic Control of the Thyroid Gland & Thyroid Evaluation
T3 and T4 cross the cell membrane easily as they are lipophilic molecules, and function via nuclear receptors in the nucleus of the cell; Thyroid hormones act on nearly every cell in the body to maintain basal metabolic rate, increases heart rate, cardiac output and ventilation rate; help to regulate long bone growth (synergy with growth hormone); neuronal maturation & brain development; increase the body's sensitivity to catecholamines (such as adrenaline); proper development and differentiation of all cells of the human body; regulate protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism affecting how human cells use energetic compounds; leads to heat generation in humans; stimulates vitamin metabolism; the thyronamines function via some unknown mechanism to inhibit neuronal activity; this plays an important role in the hibernation cycles of mammals and the moulting behaviour of birds.
Thyroid Hormones
T4 (thyroxine) 3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine
T4 is converted to T3 in target tissues
T3 is 3- to 5- fold more active than T4
Thyroglobulin >>> tyrosine + iodine >>> thyroxin
Iodide is actively absorbed from the bloodstream by a process called iodide trapping, concentrated in the thyroid follicles to about thirty times its
concentration in the blood
Factors that can contribute to the inability to convert T4 to T3, including:
1. Deficiencies of zinc, selenium, iodine and iron
2. beta blockers, Dilantin and certain other drugs
3. Alcohol and pesticides
.
T3 (triiodothyronine)
rT3 (reverse T3)
Pituitary Hormones: TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
Hypothalamic Hormones: TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormones)
Thyroxine Binding Globulin
Thyroid Antibodies
Iodine
There's been a great deal of controversy among holistic and complementary practitioners regarding whether to supplement with iodine or
iodine-containing foods and herbs (such as seaweed, kelp, bladderwrack, etc.).
Excess Iodine can aggravate autoimmune thyroid conditions
With hypothyroid conditions that are not autoimmune in nature, iodine-containing foods can actually help the thyroid function better.
All of the hormones relate to the thyroid gland (comment on DHEA and Natural Progesterone)
Hypothyroidism
Risk Factors?
Family history; personal history; treatment for hyperthyroidism (radioactive iodine, surgery, antithyroid drugs); thyroid cancer surgery;
pituitary tumors; other autoimmune or endocrine disease; epstein Barr Virus or Mononucleosis; aging; pregnancy; menopause; smoking & cessation; drugs (lithium); excess iodine supplementation; excess goitrogenic foods
Symptoms: (the most common cause of many of these symptoms is poor lifestyle)
(>50%) weakness, fatigue, lethargy, cold intolerance, dry skin, decreased sweating, hair loss, inability to concentrate, memory loss,
constipation, weight gain, dyspnea, peripheral parasthesias.
(<50%) depression anorexia muscle cramps, muscle and joint pain, infertility, menorhagia and anovulation, carpal tunnel syndrome,
decreased hearing.
Clinical HypoThyroid Disease (abnormal lab is present)
Hashimoto’s Autoimmune Thyroiditis
Graves Disease
Associated autoimmune diseases
Goiter
If there is a deficiency of dietary iodine, the thyroid will not be able to make thyroid hormone leading to increased production of thyroid stimulating
hormone, which causes the thyroid to enlarge (a goiter). This has the effect of increasing the thyroid's ability to trap more iodide, compensating for the iodine deficiency and allowing it to produce adequate amounts of thyroid hormone.
Myxedema
Subclinical HypoThyroid Disease (normal lab is present): this condition is not accepted by conventional medicine
Broda Barnes
Wilson’s Syndrome
Metabolic treatment of chronic fatigue (http://www.drlowe.com/)
Hyperthyroidism
Clinical
Graves Disease
Graves' disease is an autoimmune disease. It most commonly affects the thyroid, causing it to grow to twice its size or more (goiter), be overactive, with related hyperthyroid symptoms such as weight loss, frequent defecation, disturbed sleep, and irritability. It can also affect the eyes, causing bulging eyes (exophthalmos). It affects other systems of the body, including the skin and reproductive organs. It affects up to 2% of the female population, often appears after childbirth, and has a female:male incidence of 5:1 to 10:1. It has a strong hereditary component; when one identical twin has Graves' disease, the other twin will have it 25% of the time. Smoking is associated with the eye manifestations but not the thyroid manifestations. Diagnosis is usually made on the basis of symptoms, although thyroid hormone tests may be useful, particularly to monitor treatment. (WIKEPEDIA)
Medication Excess
Subclinical (?)
Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid Evaluation
Physician Relationship (who should you see for evaluation?)
Conventional Physician (endocrinologist or general practice)
Integrative Physician
Alternative Practitioner
Signs & Symptoms
Temperature - Normal axillary body temperature is between 97.4 and 98.2 degrees Fahrenheit. Temperatures below that are suggestive of low thyroid.
Lab Evaluation
T4/T3 |
TSH |
T4 |
T3 |
|
Normal Thyroid |
Normal Range |
Normal 0.4-4.5 mIU/L |
Normal T4 = 5.6-13.7 mcg/dl FT4 = 0.8-1.5 ng/dl |
Normal T3= 87-180 ng/dl FT3 = 230-420 pg/d; |
Hypothyroid (primary) |
Decreased |
Increased Mild Moderate Severe |
||
Hyperthyroid |
Increased |
Decreased |
||
Thyroid Antibodies (anti-peroxidase, anti-thyroglobulin)
Iodine Patch Test (reference #3)
From the published data, the skin iodine patch test is not a reliable method to assess whole body sufficiency for iodine. Many factors play a role in the disappearance of the yellow color of iodine from the surface of the skin. For example, if iodine is reduced to iodide by the skin, the yellow color of iodine will disappear because iodide is white. In order to regenerate iodine on the skin, one needs to apply an oxidant such as hydrogen peroxide, complicating the test further. Th evaporation of iodine from the skin increases with increased ambient temperatures and decreased atmospheric pressure due to weather conditions and altitude. For example, the yellow color of iodine will disappear much faster in Denver, Colorado at 5,000 feet above sea level then Los Angeles, California at sea level, irrespective of the amount of bioavailable iodine. The iodine/iodide loading test is much more accurate and it is now available from two laboratories: FFP Laboratories, 80 Doctors Dr., Suite 3, Hendersonville, NC 28292 Phone: 887-900-5556 / Fax: 828-684-3253 Doctor’s Data Inc., 3755 Illinois Avenue, St. Charles, IL 60174, Phone: 800-323-2784 / Fax: 630-587-7860
Thyroid Medication
Synthroid, Unithroid, Levoxyl, generic :
Levothyroxine (synthetic stereoisomer of T4 with longer ½ life = QD dosing)
Cytomel: Liothyronine (synthetic T3)
Thyrolar: Levothyroxine + Liothyronine
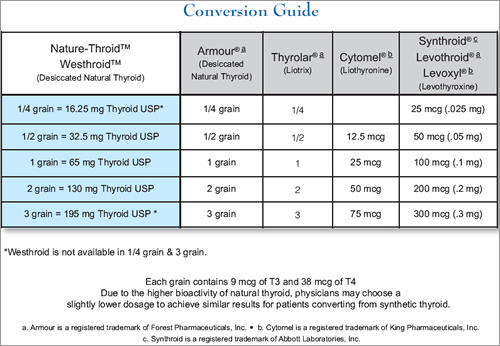
Armour / Naturethroid / Westhroid (USP dessicated natural thyroid)
Porcine glandular (1 grain = 60 mg = 9 micrograms T3 + 38 micrograms T4
(80/20 as compared to the human 93/7)
Compounded Thyroid Meds
Natural T3 + T4 in slow release capsule (any way you want it)
Interference with thyroid medication absorption: Excessive soy intake or supplementation; Excessive dietary fiber; Iron supplements, Aluminum Hydroxide antacids, Calcium Supplements; Medications: Cholestyramine (Questran to lower cholesterol), Sucralfate (for ulcers), Kayexalate (for high K+)
Inhibition of T4 >>> T3 conversion: Beta blockers and corticosteroids that only inhibit the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 interfere minimally with thyroid function test results; Lithium, Interferon alpha (for Hepatitis C); Cytochrome P-450 hepatic enzyme inducers (for example, rifampin, rifabutin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital) can increase the metabolic elimination of T4 and T3 by 20%, which is not clinically important in people who are euthyroid.
Medications can alter thyroid function test results in euthyroid people
| |
|
Laboratory findings |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Decreased TSH (below normal butdetectable) |
Increased TSH (usually <10 U/L) |
Increased Free T4 |
Decreased Free T4 |
Medications |
Dopamine, levodopa, bromocriptine, glucocorticoids (>0.5 mg/day dexamethasone, 100 mg/day hydrocortisone), octreotide, amphetamines |
Metoclopramide >1 mg/kg amiodarone, iodinated contrast media |
IV furosemide >80 mg/day, nonsteroidal agents (salicylates >2 g/day, salsalate >1.5-3 g/day, diclofenac, naproxen), IV heparin, amiodarone, iodinated contrast media |
Phenytoin, carbamazepine |
TSH = thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropin); FT4 = free thyroxine; IV = intravenous. |
||||
West J Med. 2000 February; 172(2): 102–106.
Alternative Thyroid Therapies
Supplements
Iodine -- diet and kelp (225 microgram per tablet kelp in one supplement). Soil is very iodine depleted in most areas today. Foods that contain iodine are yogurt, eggs, meat, fish and other seafood, radish, parsley, potatoes, oatmeal and bananas.
Selenium -- Many people diagnosed with hypothyroidism were found to be selenium deficient.Selenium is required to convert the T4 thyroid hormone to the active T3 form. Also a good antioxidant at 200 micrograms daily.
Tyrosine – amino acid source for thyroid hormone production. 500mg twice a day on an empty stomach
Bladderwrack = kelp ![]() -- Bladderwrack is a seaweed that is a rich source of iodine. Traditionally it has been used for weight loss and hypothyroidism. The low incidence of goiter in maritime people has been attributed to the iodine in bladderwrack. It also contains the minerals potassium, magnesium, calcium, iron, zinc, etc. Bladderwrack is thought to stimulate the thyroid gland increasing metabolism.
-- Bladderwrack is a seaweed that is a rich source of iodine. Traditionally it has been used for weight loss and hypothyroidism. The low incidence of goiter in maritime people has been attributed to the iodine in bladderwrack. It also contains the minerals potassium, magnesium, calcium, iron, zinc, etc. Bladderwrack is thought to stimulate the thyroid gland increasing metabolism.
Coconut Oil – Medium Chain Triglycerides. : J Nutr. 2002 Mar;132(3):329-32. http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/content/full/132/3/329
Physiological effects of medium-chain triglycerides: potential agents in the prevention of obesity. St-Onge MP, Jones PJ.
School of Dietetics and Human Nutrition, McGill University, Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue, Quebec, Canada,
Fats varying in fatty acid chain lengths are metabolized differently (1–8
). Medium-chain triglycerides (MCT),3 containing 6–12 carbon fatty acids, differ from long-chain triglycerides (LCT), which have fatty acids of > 12 carbons, in that they are absorbed directly into the portal circulation and transported to the liver for rapid oxidation (1
). LCT, however, are transported via chylomicrons into the lymphatic system, allowing for extensive uptake into adipose tissue. Therefore, it has been hypothesized that the rapid metabolism of MCT may increase energy expenditure (EE), decrease their deposition into adipose tissue and result in faster satiety. The objective of the present article is to review literature concerning the effects of MCT on EE, fat deposition and food intake as a means to establish the potential efficacy of MCT in the prevention of obesity in humans.
DHEA: Some researchers believe that supplementation with DHEA might assist in stimulating thyroid production and alleviating symptoms.
Herbs
There are no herbs (plant chemicals) that contain thyroid hormone. Herbs may be helpful in supporting thyroi function
Adaptogens
Rhodiola (Rhodiola Rosea), Ginseng (Panax Ginseng), Holy Basil (Ocinum sanctum), Maca (Lepidium meyenii), Ashwaganda (Withania Somifera), Cordyceps mushroom (C. Sinensis), Reishi mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum), Agaricus mushroom (A. glazei)
Herbs used to support thyroid function: Bayberry, black cohosh, goldenseal, Siberian ginseng, astragalus, saw palmetto berry, triphala, \
ashwagandha, guggul, skullcap, and maca.
Ayurvedic: Guggulsterone: Commiphora Mukul (guggle Tree)
Studies have shown that guggulsterone extracts from the Indian herb Commiphora Mukul can increase the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood. The herb is especially effective in increasing the ratio of the active T3 form of thyroid (triiodothyronine) to T4 (thyroxine). A corresponding and significant decrease in normal liver damage by free radicals was noticed, which is most interesting considering the fact that the liver is the principal site where T4 thyroid is stored and T3 thyroid is generated. Due to the natural increase in thyroid hormone function, and possibly other factors, guggulsterones have been used to treat overweight patients. During those double-blind clinical studies, a significant fall in serum cholesterol was noticed. Thyroid hormone studies with forskolin extract of the Indian herb Commiphora Mukul, have shown increased thyroid production.
Influence of Diet
Goitrogenic foods: (these must be taken raw in large amounts over a prolonged period of time to cause a problem
brussel sprouts, rutabaga, turnips, kohlrabi, radishes,cauliflower, african cassava, millet, babassu, cabbage, kale, soy products.
Consume foods naturally high in B vitamins, such as whole grains, nuts, and seeds, and iodine (fish, seaweed, vegetables and root vegies)
Chlorine, fluorine, and fluoride are chemically related to iodine, and compete with it, blocking iodine receptors in the thyroid gland.
Energy Medicine
Energy Body
Fifth Chakra
Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ayurvedic Medicine, Homeopathy
Bodywork
Exercise, Yoga, Movement Therapies
references
- http://thyroid.about.com/ (Mary Shomon) Living Well With Hypthyroidism
- https://www.drbrownstein.com/home.asp Overcoming Thyroid Disorders
- http://www.optimox.com/pics/Iodine/updates/UNIOD-02/UNIOD_02.htm
- http://www.drlowe.com/ The Metabolic Treatment of Fibromyalgia
- http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/t/thyroid/prevalence.htm
- Textbook of Primary Care Medicine, second edition. John Noble, M.D. (editor)
- Coconut Oil & Medium Chain Triglycerides http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/content/full/132/3/329
![]()
Home ![]() Intro
Intro ![]() Medicine Pages
Medicine Pages ![]() Moontime & Menopause Medicine Wheel
Moontime & Menopause Medicine Wheel
Ritual & Ceremony ![]() Temple of Health Radio Show
Temple of Health Radio Show ![]() Links & References
Links & References
![]() Events
Events ![]() Divine
Light Farms
Divine
Light Farms ![]()
